Greenhouse gases in the atmosphere 135990-Greenhouses gases in the atmosphere
Greenhouse gases (GHGs) trap the infrared radiation coming from the Sun and prevent it from escaping to outer space They reradiate it back to Earth's atmosphere They are responsible for increasing the temperature of the atmosphere Carbon dioxide (CO 2 ), methane (CH 4 ), nitrous oxide (N 2 O), Ozone (O 3 ), and chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs), along with water vapour are knownSome greenhouse gases occur naturally and enter the atmosphere as a result of both natural processes (such as decomposition of organic matter) and human activity (such as burning fossil fuels and agriculture) Greenhouse gases that occur both naturally and from human activities include water vapor, carbon dioxide (CO 2),"Dumping greenhouse gases into the atmosphere makes the atmosphere more humid And since water vapor is itself a greenhouse gas, the increase in humidity amplifies the warming from carbon dioxide" Specifically, the team found that if Earth warms 18 degrees Fahrenheit, the associated increase in water vapor will trap an extra 2 Watts of

The Greenhouse Effect Climate Matters
Greenhouses gases in the atmosphere
Greenhouses gases in the atmosphere-Greenhouse gases have very different warming effects one tonne of methane does not have the same impact on warming as one tonne of CO 2Carbon dioxide equivalents (CO 2 e) attempt to convert the warming impact of the range of greenhouse gases into a single metric This is done by multiplying each gas by its 100year 'global warming potential' value the amount of warming oneThe atmosphere today contains more greenhouse gas molecules, so more of the infrared energy emitted by the surface ends up being absorbed by the atmosphere Since some of the extra energy from a warmer atmosphere radiates back down to the surface, Earth's surface temperature rises By increasing the concentration of greenhouse gases, we are




Heat Trapping Gases Climate Communication
2 days ago # The three greenhouse gases of greatest concern are carbon dioxide, nitrous oxide, and methane Greenhouse gases trap heat in the atmosphere to keep the Earth warm, which is known as the greenhouseGreenhouse gases are gases—like carbon dioxide (CO 2 ), methane, and nitrous oxide—that keep the Earth warmer than it would be without them The reason they warm the Earth has to do with the way energy enters and leaves our atmosphere When energy from the sun first reaches us, it does so mainly as lightGreenhouse gases The atmosphere is largely transparent to the Sun's energy, most of which arrives in the form of light At the Earth's surface, this energy is partly reflected back out to space, and partly absorbed and reradiated as heat The greenhouse gases in the atmosphere can both absorb and reradiate much of the outgoing heat energy
Main Greenhouse Gases Multiple gases contribute to the greenhouse effect that sets Earth's temperature over geologic time Small changes in the atmospheric concentration of these gases can lead to changes in temperature that make the difference between ice ages when mastodons roamed the Earth, and the sweltering heat in which the dinosaurs lived4 rows Greenhouse gases from human activities are the most significant driver of observed climateAtmosphere Greenhouse gases can also reabsorb solar radiation reflected or reemitted from Earth's surface, trapping the heat in our atmosphere instead of letting it escape to space The Greenhouse Effect is a natural process essential for life on Earth, because it
Although greenhouse gases make up only about 1 percent of the Earth's atmosphere, they regulate our climate by trapping heat and holding it in a kind of warmair blanket that surrounds the planet Carbon Brief and Duncan Clark Mon 00 EST Aside from water vapour, the four principal greenhouse gases are carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), nitrous oxide (N2O) and theThe AGGI in was 147, which means that we've turned up the warming influence from greenhouse gases by 47% since 1990;



1




Percentage Of Greenhouse Gases In The Atmosphere Download Scientific Diagram
Greenhouse gases are gases in Earth's atmosphere that trap heat They let sunlight pass through the atmosphere, but they prevent the heat that the sunlight brings from leaving the atmosphere The main greenhouse gases are Water vapor Carbon dioxide MethaneGreenhouse gas emissions are greenhouse gases vented to the Earth's atmosphere because of humans the greenhouse effect of their 50 billion tons a year causes climate changeMost is carbon dioxide from burning fossil fuels coal, oil, and natural gasThe largest polluters include coal in China and large oil and gas companies, many stateowned by OPEC and Russia Greenhouse gases include carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), nitrous oxide (N2O), ozone (O3), and fluorinated gases The greenhouse effect happens when certain gases, which are known as greenhouse gases, accumulate in Earth’s atmosphere
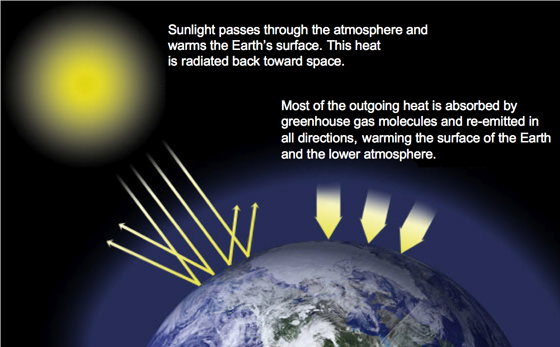



How Do Greenhouse Gases Trap Heat Socratic
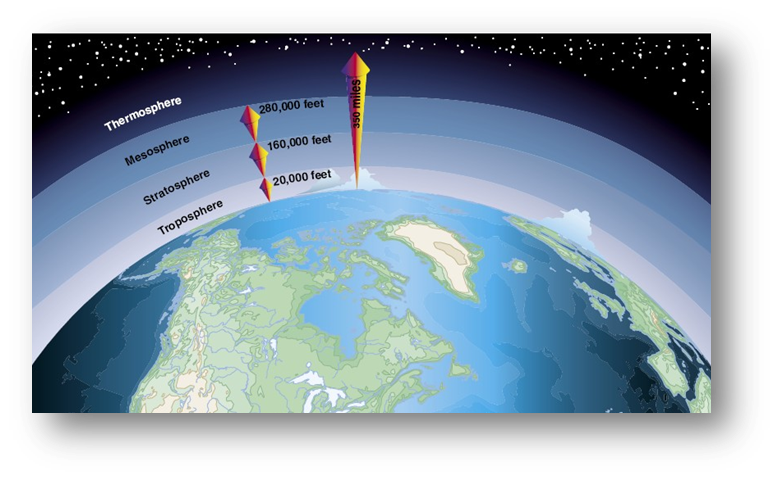



Atmosphere Greenhouse Gases Athenas
INTRODUCTION Greenhouse gases which include water vapour, carbon dioxide, nitrous oxide, halogenated flurocarbons and hydroflurocarbons (HFCs) absorbs the infrared radiation in the atmosphere and in turn makes the earth warmerOver the last 100 years, the average air temperature near the earth′s surface has risen by a little less than 1 degree Celsius or 13Greenhouse gases come from all sorts of everyday activities, such as using electricity, heating our homes, and driving around town The graph to the right shows which activities produce the most greenhouse gases in the United States These greenhouse gases don't just stay in one place after they're added to the atmosphere At the top of the troposphere, 12 miles high, ozone acts as a greenhouse gas, trapping heat In the middle of the tropsohere, ozone helps clean up certain pollutants At the bottom of the troposphere, at Earth's surface, ozone makes smog Scientists have divided the atmosphere into different layers, each with a name



Greenhouse Gas Wikipedia
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/521928855-58b5c1875f9b586046c8ee0e.jpg)



Worst Greenhouse Gases In The Atmosphere
Most of these humancaused (anthropogenic) greenhouse gas emissions were carbon dioxide (CO2) from burning fossil fuels Concentrations of CO2 in the atmosphere are naturally regulated by many processes that are part of the global carbon cycleComparing greenhouse gases All greenhouse gases absorb energy, but different gases have different effects on warming Carbon dioxide, methane and nitrous oxide remain in the atmosphere for long enough to allow them to mix together As a result, the gas concentrations are about the same around the globe, regardless of the source or location of the emissions The major Greenhouse Gas, carbon dioxide, emitted naturally and by the burning of fossil fuels, stays in the atmosphere a long time Its warming effect occurs even when the sky is clear and dry Climate scientists are so concerned about carbon dioxide because the more carbon dioxide in the atmosphere, the hotter the earth will become, changing




15 Sources Of Greenhouse Gases



Atmospheric Greenhouse Gas Concentrations European Environment Agency
A greenhouse gas is any gaseous compound in the atmosphere that is capable of absorbing infrared radiation, thereby trapping and holding heat inThe effect of greenhouse gases There are five gases of human origin that contribute most – together up to 95% of the total – to the increase in global warming Here you will discover the source of their emission, the time they spend in the atmosphere and what percentage they contribute to the greenhouse effect The Carbon Cycle Greenhouse Gases (CCGG) research area operates the Global Greenhouse Gas Reference Network, measuring the atmospheric distribution and trends of the three main longterm drivers of climate change, carbon dioxide (CO 2), methane (CH 4), and nitrous oxide (N 2 O), as well as carbon monoxide (CO) which is an important indicator of air pollution




Usgcrp Indicator Details Globalchange Gov




Esrl Global Monitoring Laboratory Education And Outreach
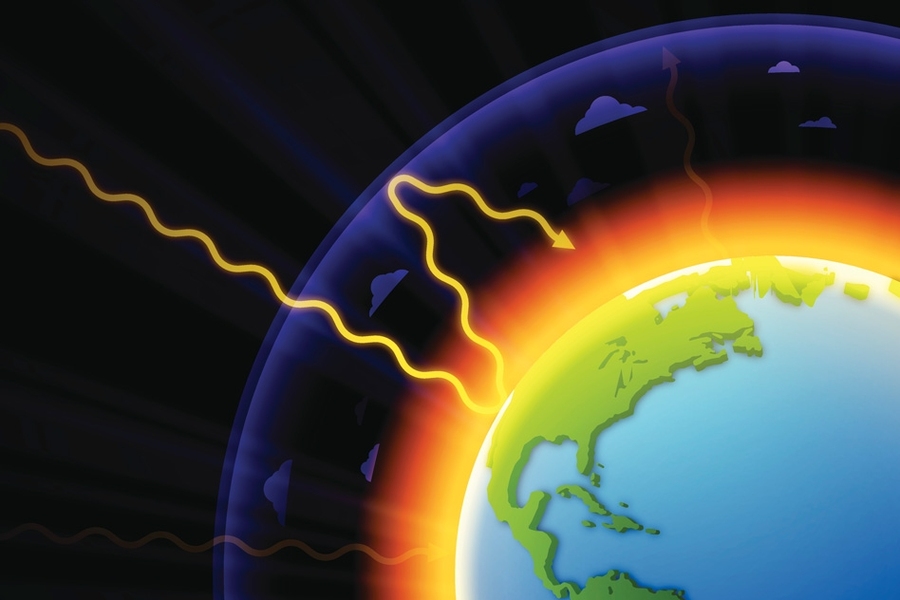
Greenhouse Effect Warming that result when the atmosphere traps heat radiating from Earth toward space Gases that contribute to the greenhouse effect include ¾ Water vapour ¾ Carbon Dioxide ¾ Methane ¾ Nitrous Oxide ENGG 413 ENVIRONMENTAL SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING Main Topic 1 Ecological Concepts 33 P a g e ¾ ChlorofluorocarbonsFluorinated Gases (HFCs, PFCs, SF 6) Fluorinated gases are emitted in smaller quantities than the other greenhouse gases, but what they lack in volume they can make up in potency and long lifespans in the atmosphere, ranging from 1270 years for HFCs to ,000 years for PFCs and about 3,0 years for SF6A greenhouse effect is a process wherein it happens when gases in the Earth's atmosphere traps the heat of the sun In return, it can make Earth warmer and provide a comfortable living environment It is a natural phenomenon that benefits human because of the suitable temperature for the development of life



Untitled Document




Greenhouse Gas Levels In Atmosphere Reach New Record United Nations Sustainable Development
Greenhouse gases include carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxides Scientists have determined that carbon dioxide's warming effect helps stabilize Earth's atmosphere Remove carbon dioxide, and the terrestrial greenhouse effect would collapse Without carbon dioxide, Earth's surface would be some 33 °C (59 °F) coolerThe greenhouse effect happens when certain gases—known as greenhouse gas es—collect in Earth's atmosphere These gases, which occur naturally in the atmosphere, include carbon dioxide, methane, nitrogen oxide, and fluorinate d gases sometimes known as chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs)Much like the glass of a greenhouse, gases in Earth's atmosphere sustain life by trapping the sun's heat These "greenhouse gases" allow the sun's rays to pass through and warm the planet but prevent this warmth from escaping the atmosphere into space




What Are Greenhouse Gases David Suzuki Foundation




The Greenhouse Effect
Graph by NOAA Climategov based on data from NOAA ESRL According to the 19 AGGI report, the combined heating influence of the longlived, humanproduced greenhouse gases is 314 Watts for every square meter of Earth's surface Just over 80 percent of that is due to carbon dioxide (66%) and methane (16%) The 'greenhouse effect' is the warming of climate that results when the atmosphere traps heat radiating from Earth toward space Certain gases in the atmosphere resemble glass in a greenhouse, allowing sunlight to pass into the 'greenhouse,' but blocking Earth's heat from escaping into space The gases that contribute to the greenhouse effect include water vapor,The most abundant greenhouse gas, but importantly, it acts as a feedback to the climate Water vapor increases as the Earth's atmosphere warms, but so does the possibility of clouds and precipitation, making these some of the most important feedback mechanisms to the greenhouse effect Carbon dioxide (CO 2 )



Greenhouse Gases And Temperature
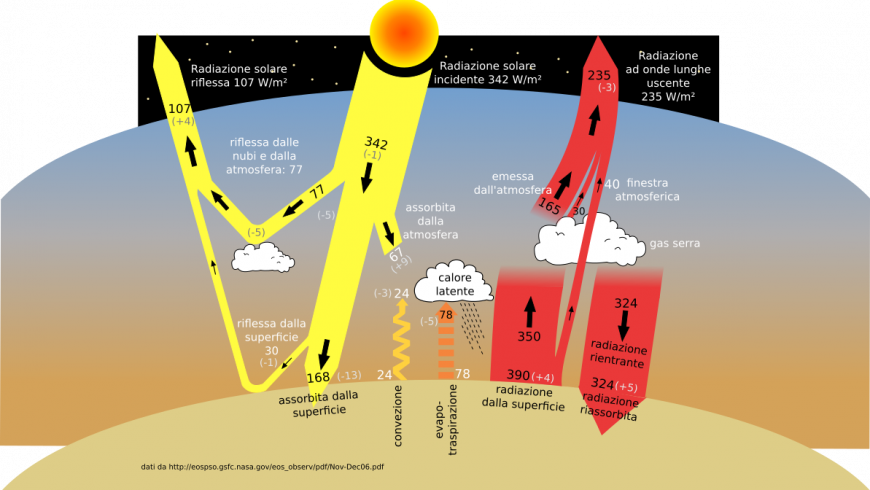



Greenhouse Gases What Are They What Can We Do To Reduce Emissions
Greenhouse gas molecules in the atmosphere absorb light, preventing some of it from escaping the Earth This heats up the atmosphere and raises the planet's average temperature What do CO 2, methane, and water vapor have in common?It took ~240 years for the AGGI to go from 0 to 1, ie, to reach 100%, and 30 years for it to increase by another 47% In terms of CO 2 equivalents, the atmosphere in contained 504 ppm, of which 412 is CO 2 alone The rest comes from otherGreenhouse gases in the atmosphere absorb heat energy and prevent it escaping into space This keeps the Earth warmer than it would be without these gases Greenhouse gases are not a




Greenhouse Gas Levels In Atmosphere Reach New Record World Meteorological Organization




Air Pollution Greenhouse Gases Britannica



The Greenhouse Effect




The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Global Warming Ozcoasts




Explained Greenhouse Gases Mit News Massachusetts Institute Of Technology
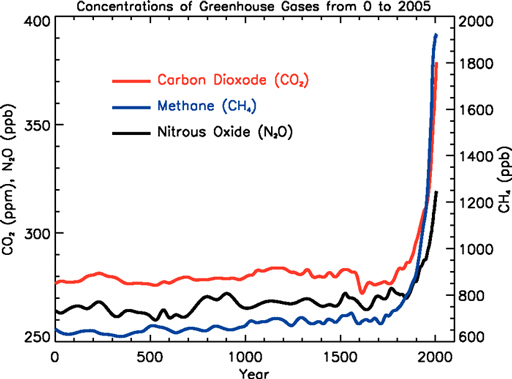



Olcreate Contextenvt 1 0 Study Session 9 Introduction To Climate Change 9 3 2 How Do Greenhouse Gases Contribute To Climate Change




Greenhouse Gases Copernicus




The Greenhouse Effect World101
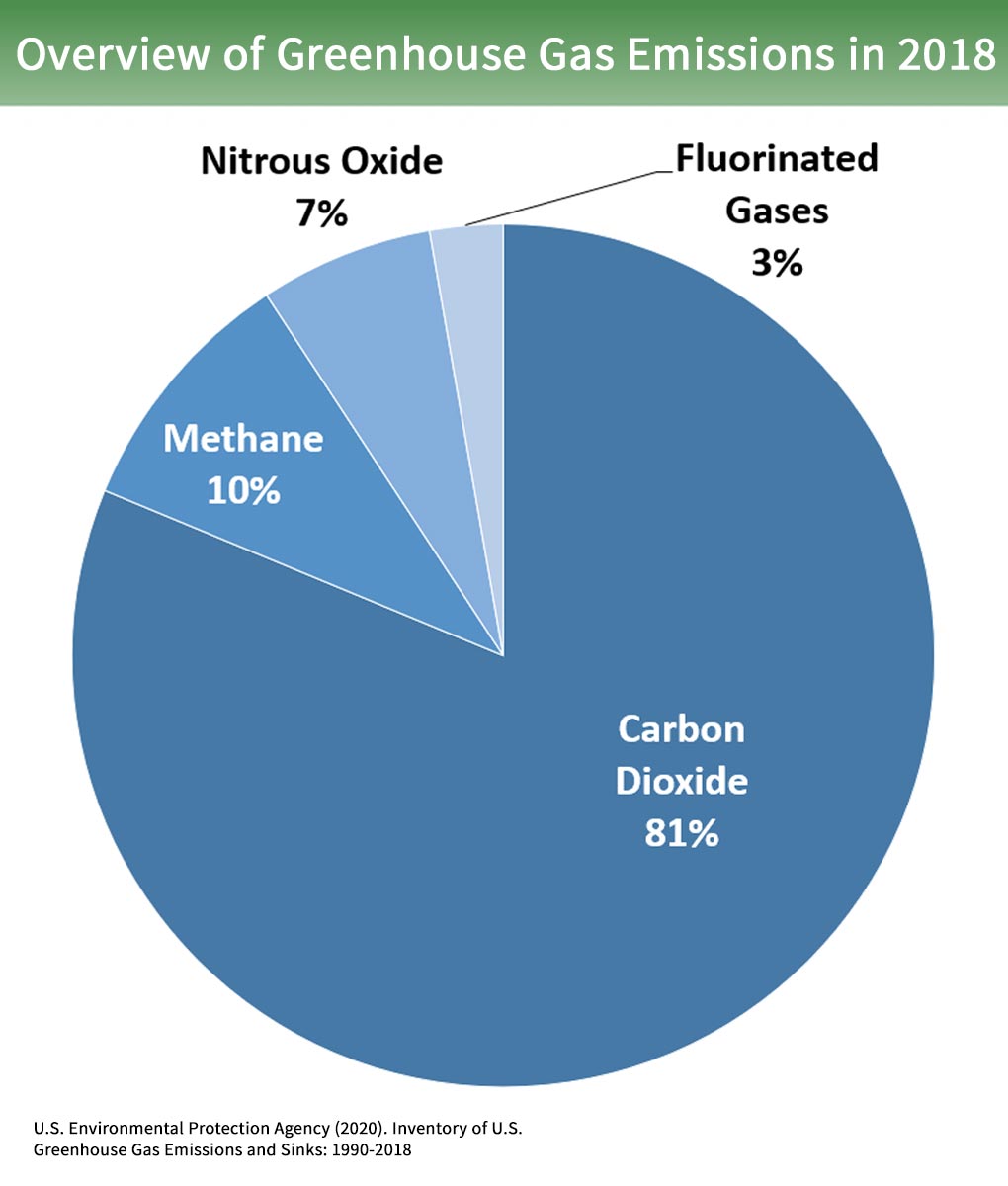



Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Greenhouse Gas Ghg Emissions Us Epa
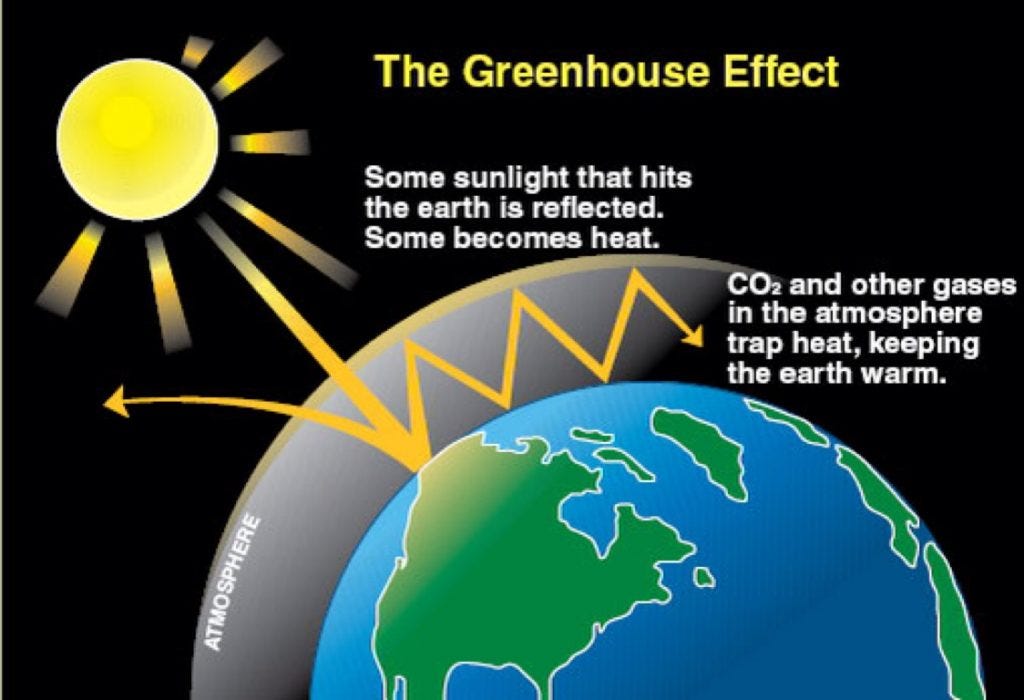



Greenhouse Effect Advantages And Disadvantages By Tutorbin Medium



1
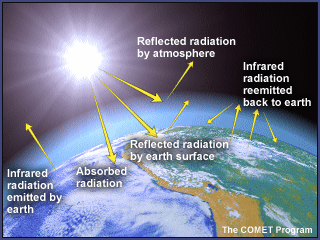



The Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Gases




Causes And Consequences Of A Warming Planet Agricultural Marketing Resource Center
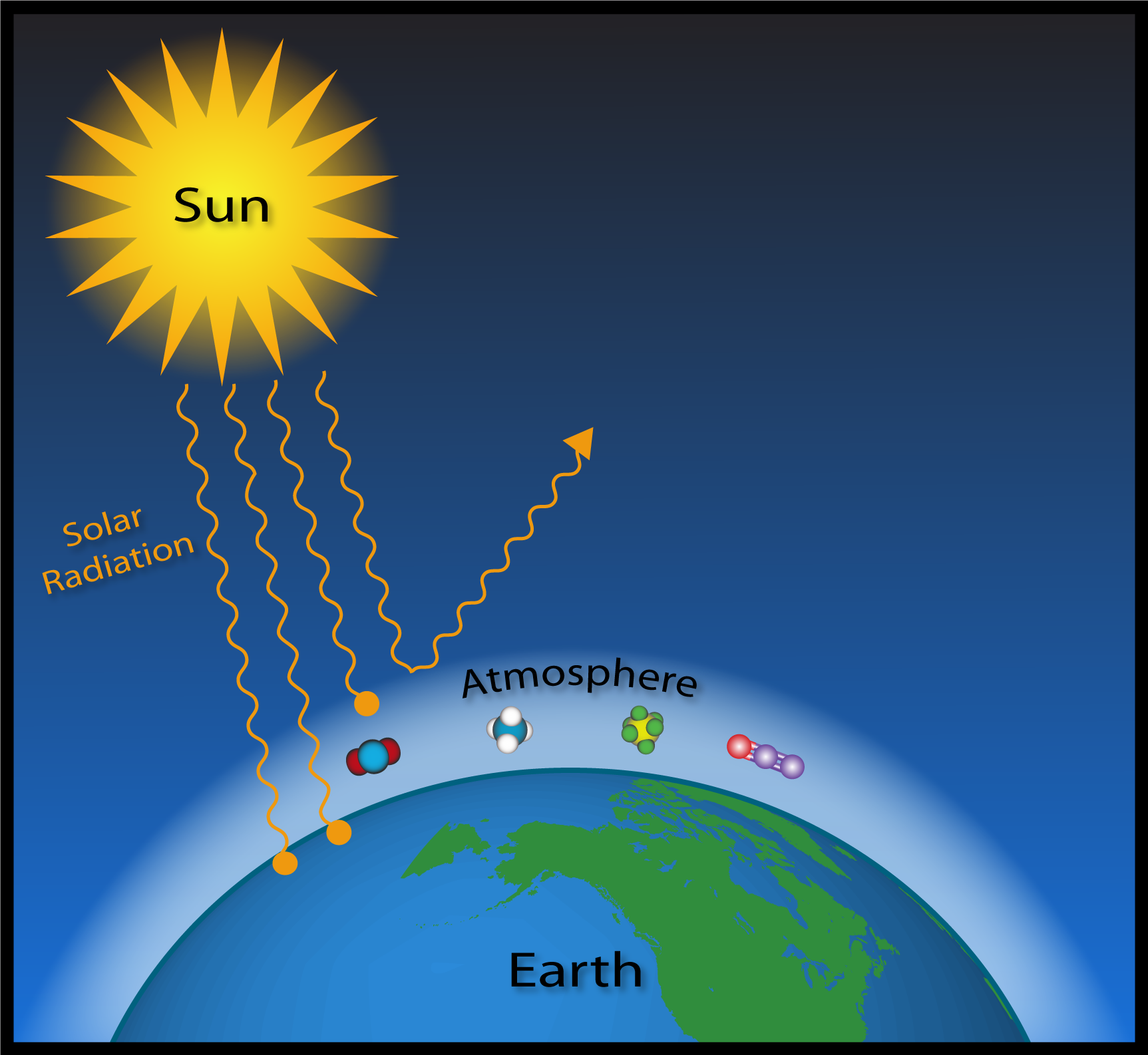



Greenhouse Gasses Captain John Smith Chesapeake National Historic Trail U S National Park Service



Greenhouse Gases




Greenhouse Gases Are Rapidly Changing The Atmosphere Climate Central




Climate Explained What Earth Would Be Like If We Hadn T Pumped Greenhouse Gases Into The Atmosphere



Atmo336 Spring 21



Atmospheric Greenhouse Gas Concentrations European Environment Agency




Greenhouse Gas Levels In Atmosphere Hit New High Un



1




Greenhouse Effect 101 Nrdc



Volcanoes Greenhouse Gases And Temperature Change
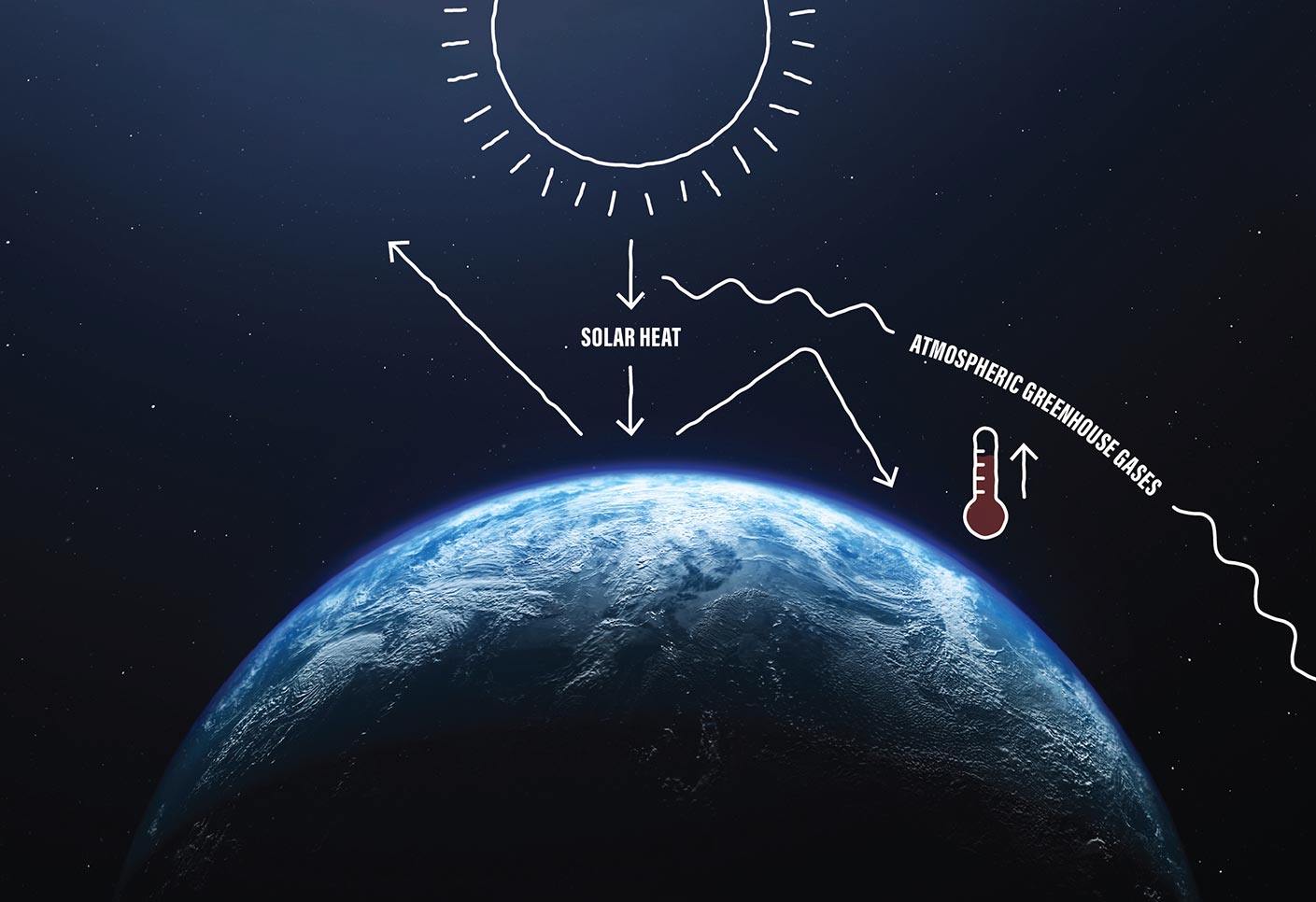



Nasa At Your Table Where Food Meets Methane And The Greenhouse Effect




Percentage Share Of Greenhouse Gases In The Earth Atmosphere 5 Download Scientific Diagram



Greenhouse Gases




What Is A Greenhouse Gas 360training




Greenhouse Gas Emissions Wikipedia




Greenhouse Gas Concentrations Surge To New Record World Meteorological Organization
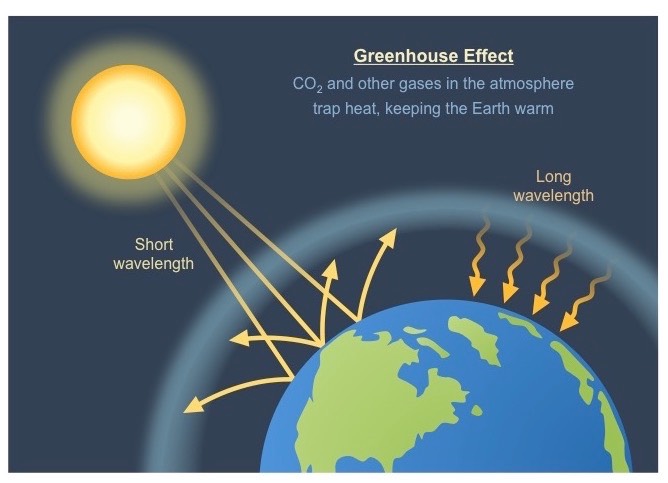



Greenhouse Gases Is It Just A Lot Of Hot Air Thrive Blog




Greenhouse Gases Causes Sources And Environmental Effects Live Science
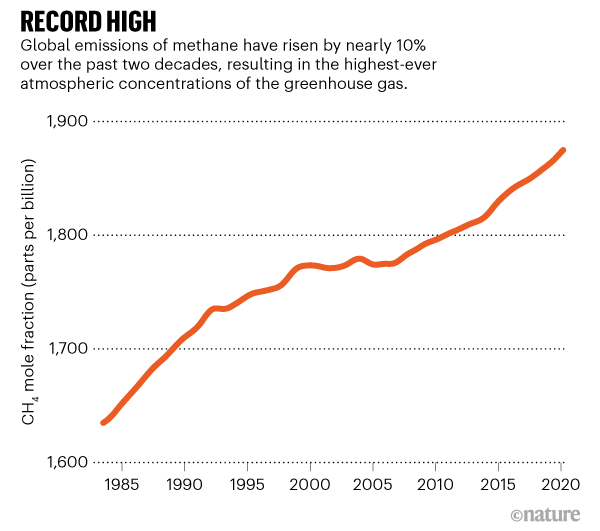



Global Methane Levels Soar To Record High



Climate Science Investigations South Florida Energy The Driver Of Climate




Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa




Greenhouse Gas Concentrations In Atmosphere Reach Yet Another High World Meteorological Organization




Greenhouse Gas Emissions Caltech Science Exchange




Greenhouse Gas Wikipedia
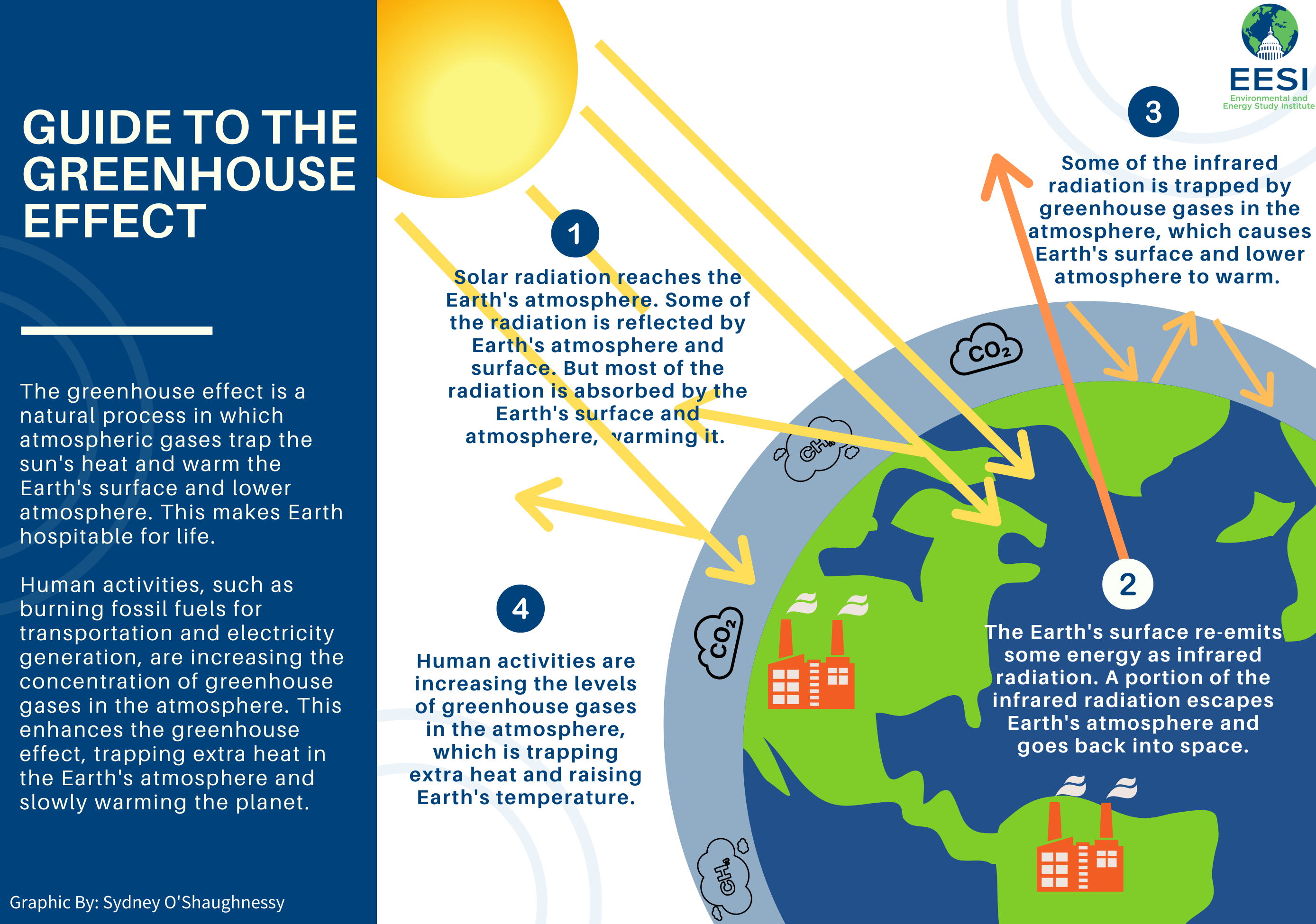



Global Warming Climate Change Frequently Asked Questions Faq Eesi




Greenhouse Gases A Student S Guide To Global Climate Change Us Epa
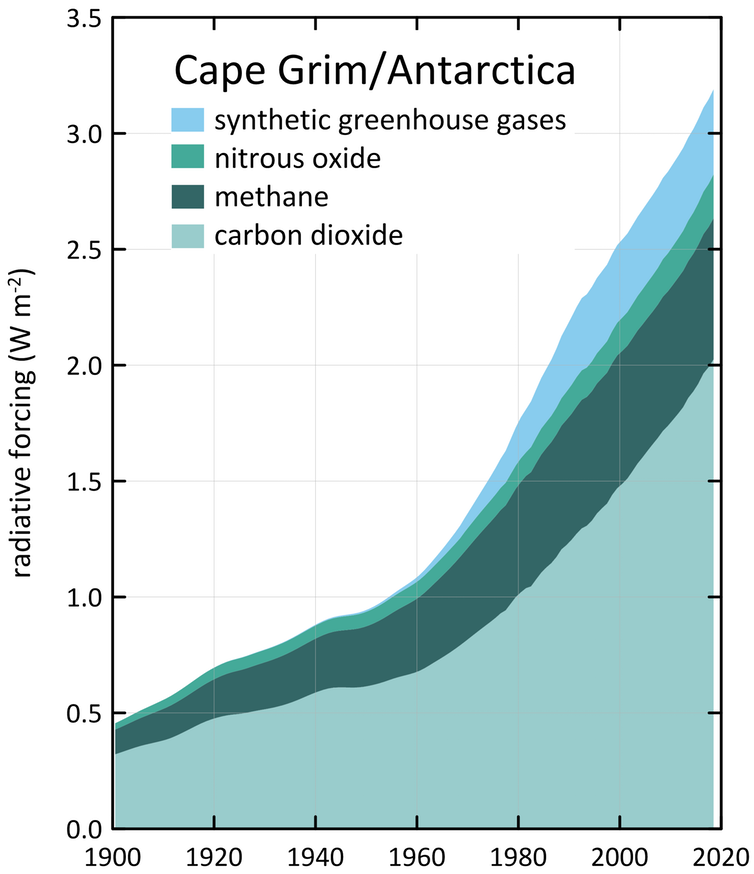



Why There S More Greenhouse Gas In The Atmosphere Than You May Have Realised Csiroscope
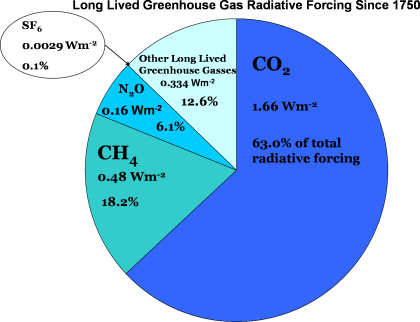



Noaa Esrl Global Monitoring Laboratory



Climate Science Investigations South Florida Energy The Driver Of Climate




Banning The Super Greenhouse Gas Environment All Topics From Climate Change To Conservation Dw 17 10 16




Care4air Greenhouse Gases




Carbon Dioxide Methane Nitrous Oxide And The Greenhouse Effect Conservation In A Changing Climate



Greenhouse Gases




Atmosphere Climate Environment Information Programme
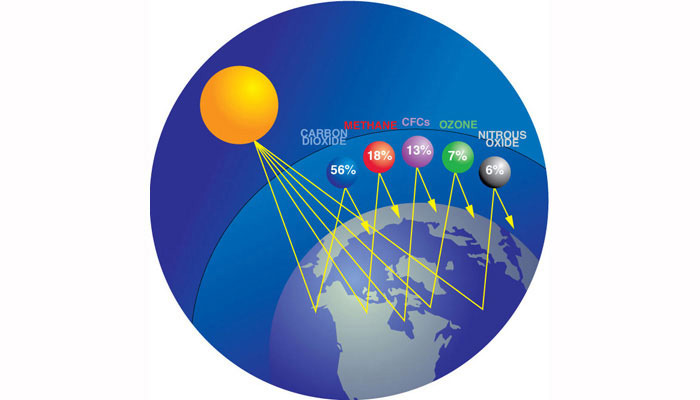



Greenhouse Gases Earth Sciences Quiz Quizizz




What Is Nitrous Oxide And Why Is It A Climate Threat Inside Climate News



Atmospheric Greenhouse Gas Concentrations European Environment Agency




Carbon Dioxide In The Atmosphere Is At A Record High Here S What You Need To Know
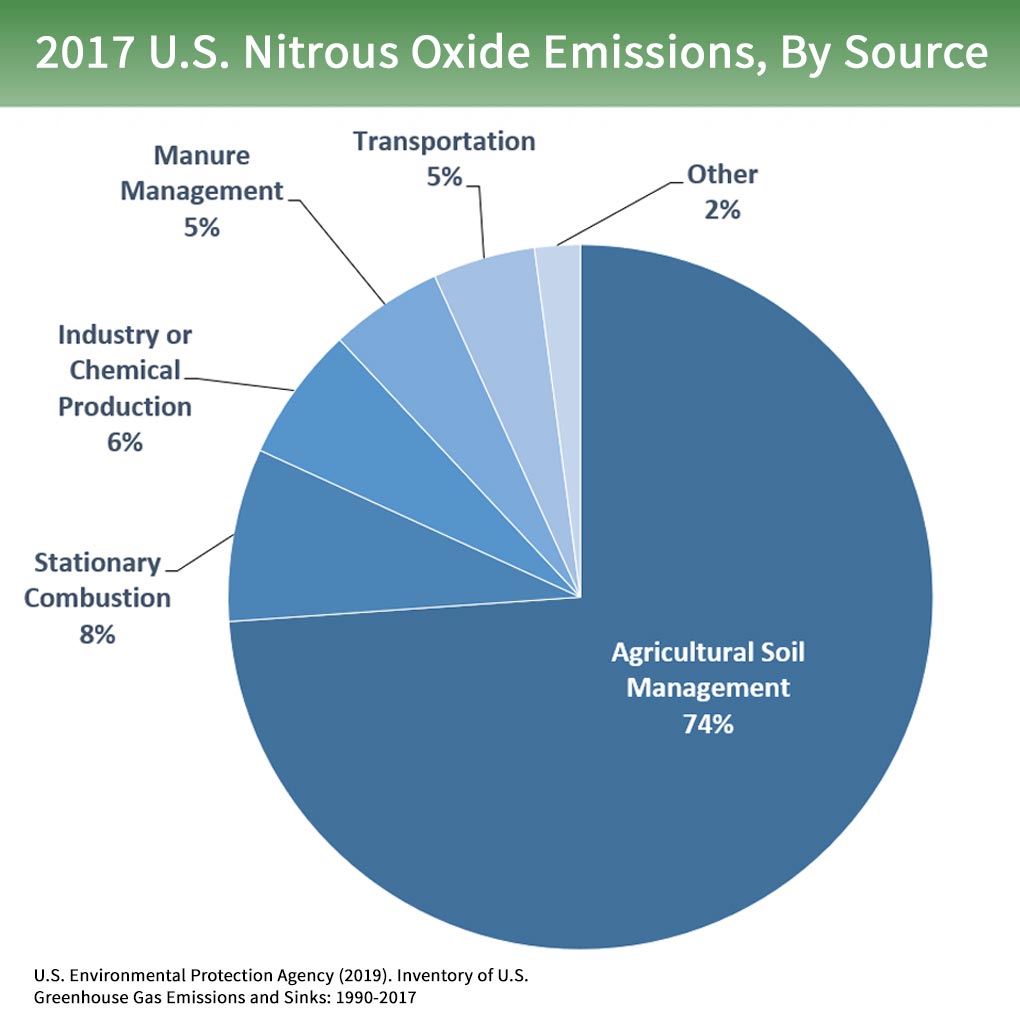



The Greenhouse Gas No One S Talking About Nitrous Oxide On Farms Explained Civil Eats




The Greenhouse Effect Climate Matters




What Is Climate Change Climate Assembly




5 Notorious Greenhouse Gases Britannica




Greenhouse Effect And Greenhouse Gases Youtube
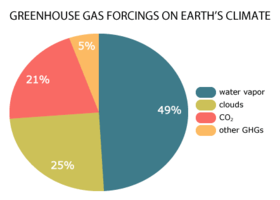



Which Are The Most Common Greenhouse Gases In The Atmosphere Socratic




The Greenhouse Effect Explained




Heat Trapping Gases Climate Communication




Atmospheric Concentrations Of The Three Main Greenhouse Gases Carbon Download Scientific Diagram
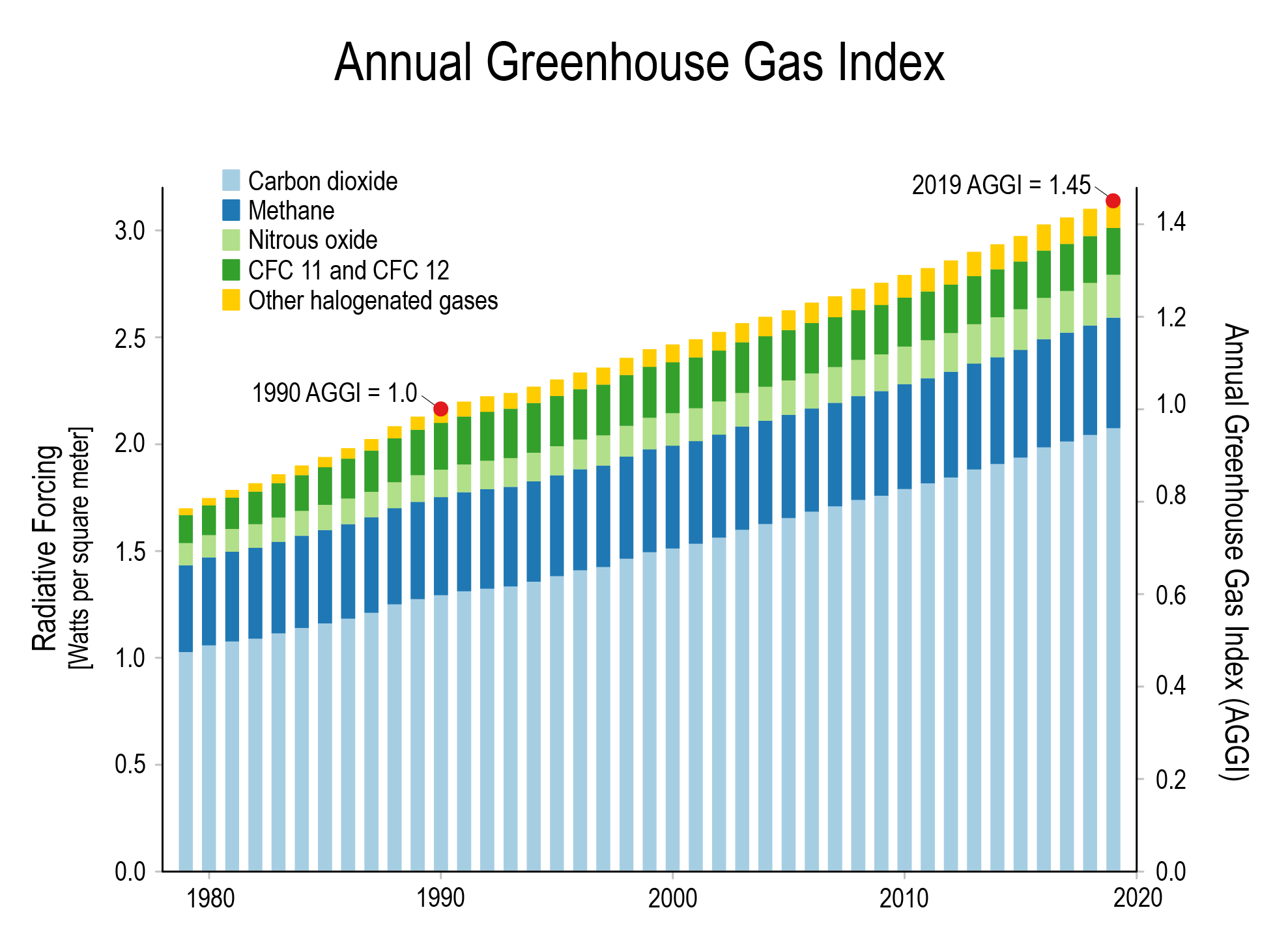



Climate Change International Ccs Knowledge Centre
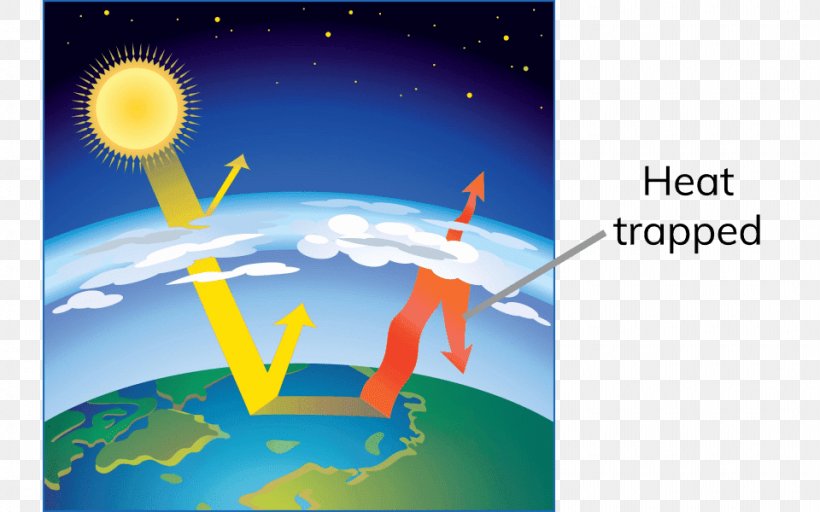



Earth Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Gas Atmosphere Png 960x600px Earth Atmosphere Atmosphere Of Earth Brand Climate Download



Greenhouse Gases




Greenhouse Effect 101 Nrdc




Greenhouse Gases American Chemical Society




The Greenhouse Effect Nasa Space Place Nasa Science For Kids




How Greenhouse Gases Influence Climate The Weather Gamut




The Greenhouse Effect British Geological Survey




What Is The Greenhouse Effect Nasa Climate Kids



Simple




The Science Hoosier Environmental Council




1zrlfbmrqd Vwm
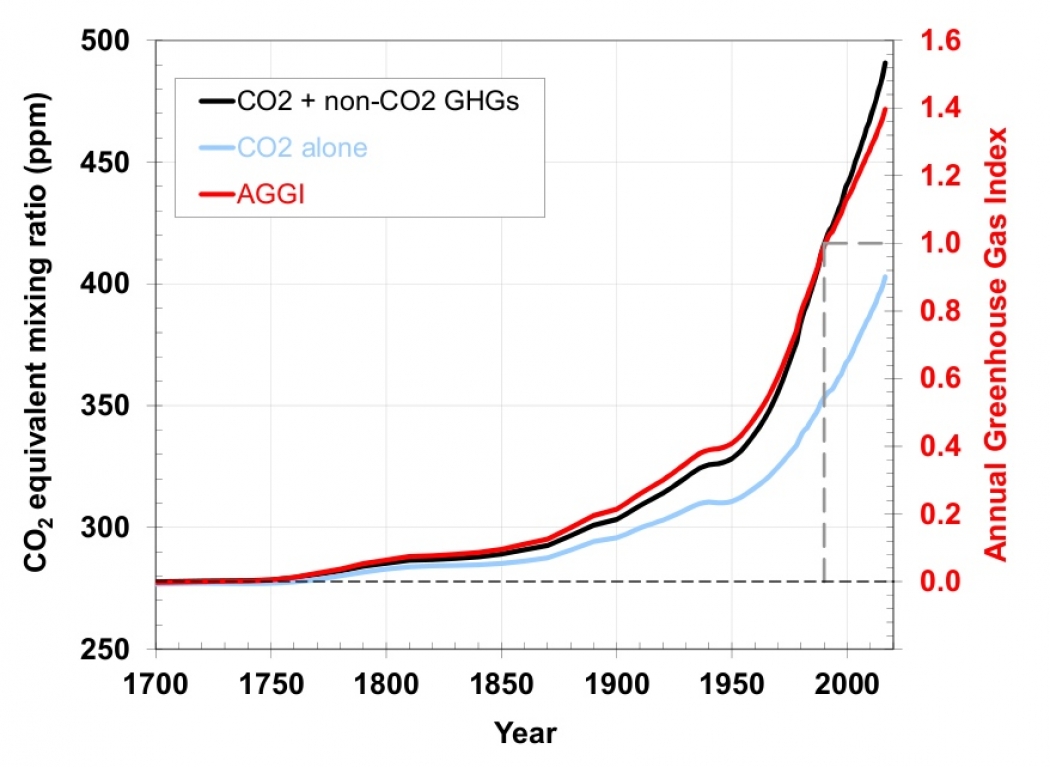



Greenhouse Gases Are Rapidly Changing The Atmosphere Climate Central
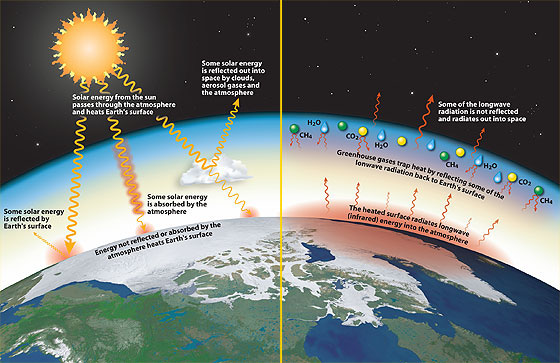



Too Much Of A Good Thing
.png)



Greenhouse Effect Energy Education




Greenhouse Gases In Atmosphere Greenhouse Gases Favorite Questions Global




Greenhouse Gases U S Energy Information Administration Eia




Greenhouse Gases Are Components Of The Atmosphere That Contribute To The Greenhouse Effect




Explainer Global Warming And The Greenhouse Effect Science News For Students




If Emissions Of Greenhouse Gases Were Stopped Would The Climate Return To The Conditions Of 0 Years Ago Royal Society




Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa



Greenhouse Gas Basics 148 Msu Extension



The Greenhouse Effect
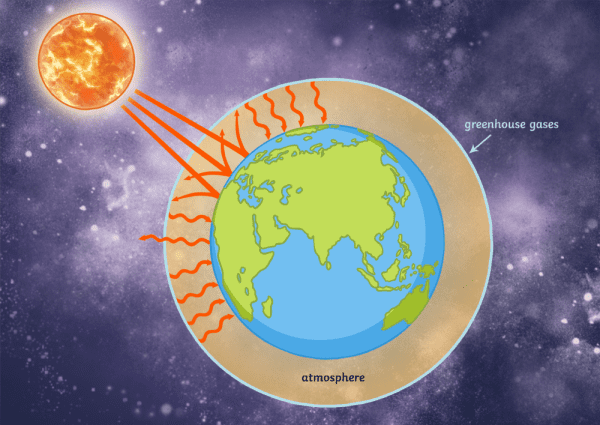



What Are Greenhouse Gases Answered Twinkl Teaching Wiki



Atmospheric Greenhouse Gas Concentrations European Environment Agency



Greenhouse Gas Global Greenhouse Warming
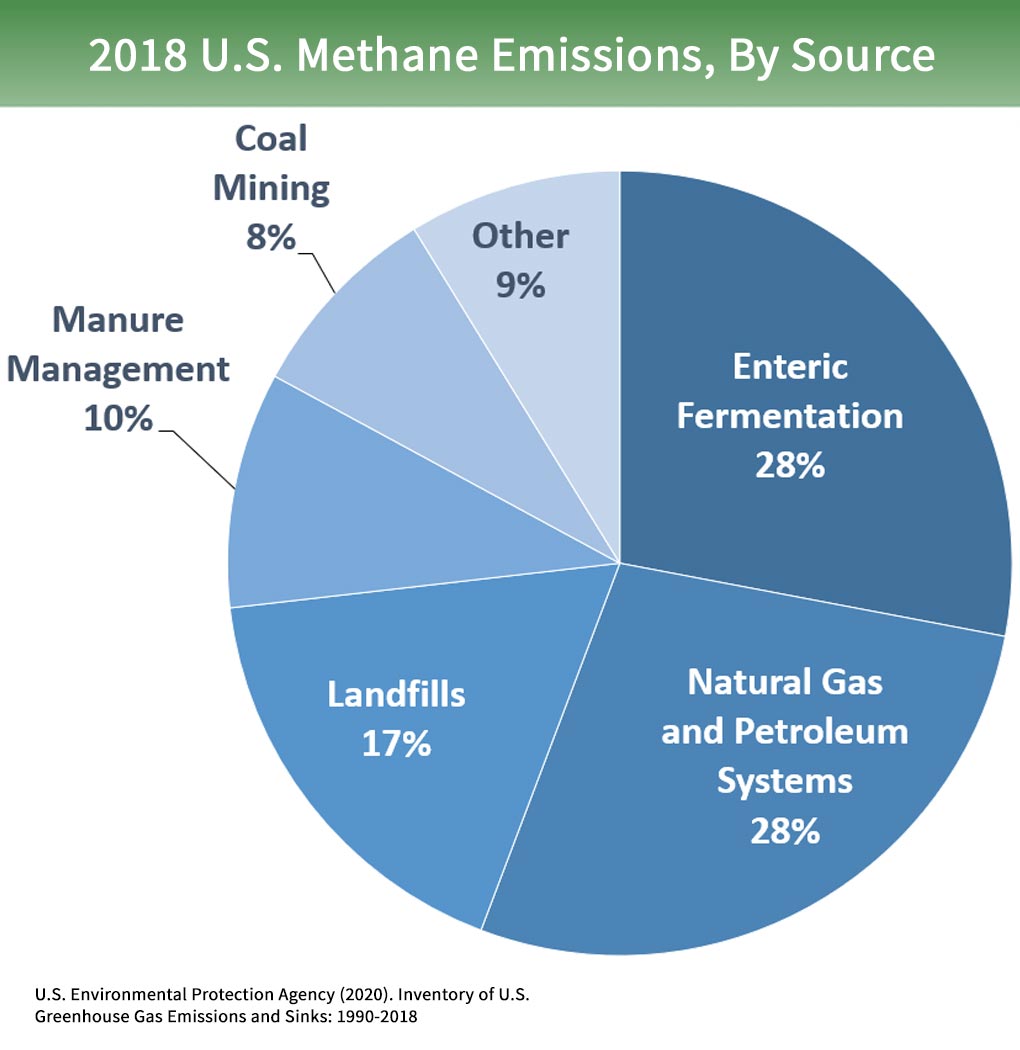



Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Greenhouse Gas Ghg Emissions Us Epa




Greenhouse Gases Bioninja
コメント
コメントを投稿